Cloud data Center (Haiwell)
In the past, when connecting various devices to communicate with each other, many people probably thought that there was only a connection through signal cables through a serial port. Whether it is the RS-232, RS-485, RS-422 standard, they can connect various devices and communicate with each other through signal cables. But all of the communication mentioned above has a limitation, which is "the distance between devices". If the devices that we want to connect and communicate with are very far apart, we will not be able to use signal cables to connect because there will be "signal loss". In addition, the cost of running signal cables is very high, whether it is the cost of signal cables, the cost of installing pipes and wiring equipment.
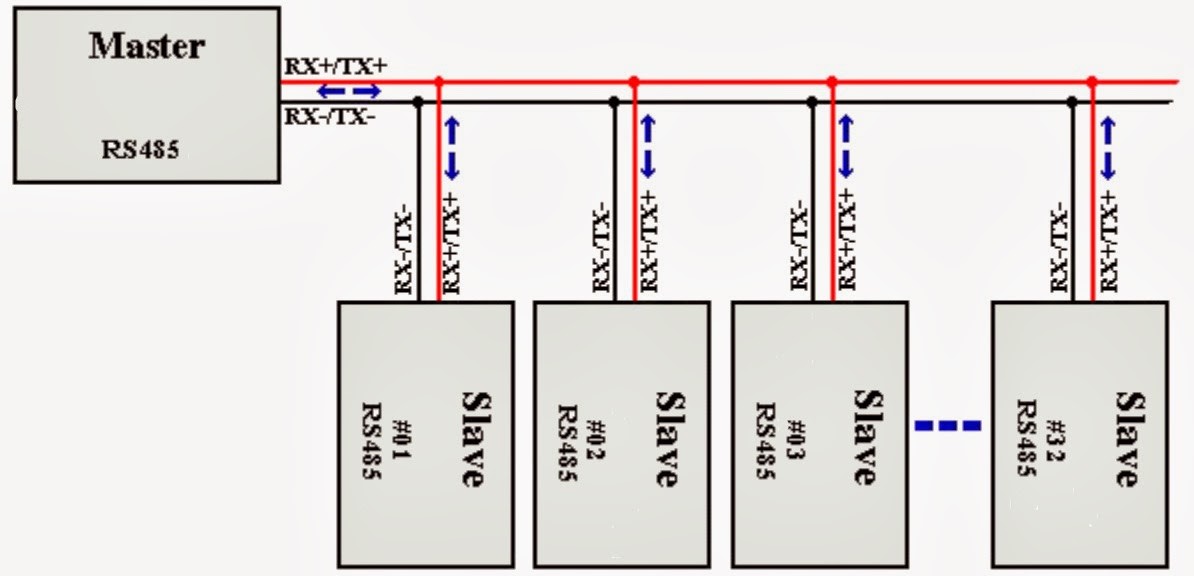
Figure 1.1. Wired connection diagram using RS-485 method
At present, there are many forms of wireless connections for us to choose from, such as MQTT, Haiwell Cloud Data Center, LoRaWAN, etc. Today we will introduce the connection of devices via a wireless network called "Haiwell Cloud Data Center" that is convenient, easy to use, easy to access, not difficult to use, and most importantly, Haiwell Cloud Data Center is open for "free use, no charge" for all who use "Haiwell" brand devices.
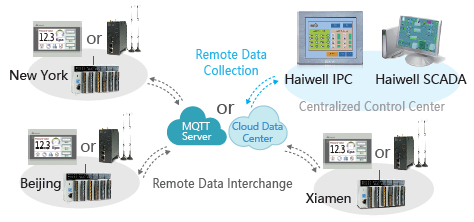
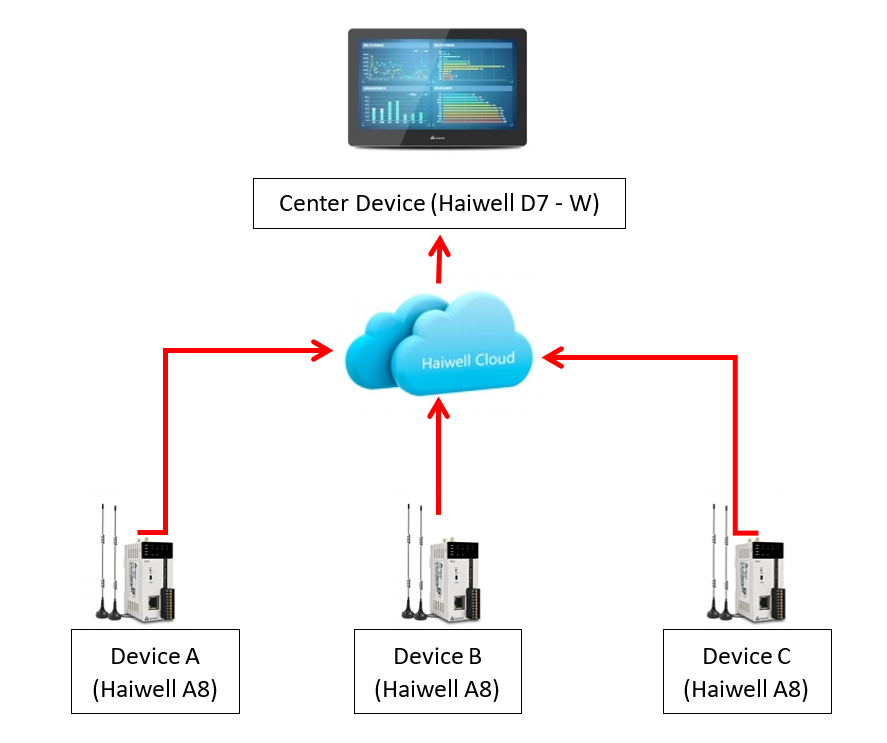
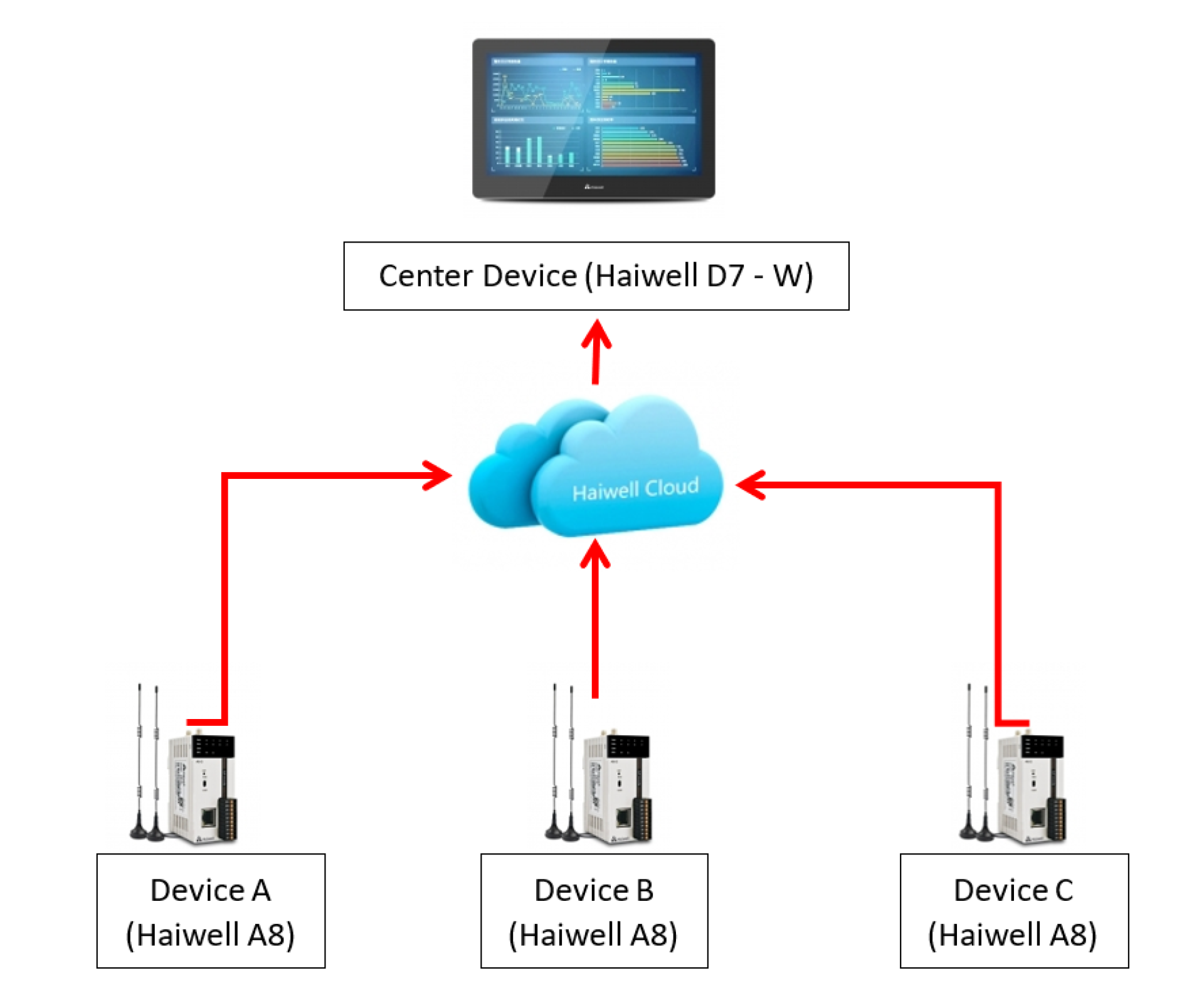
Figure 1.2. Device connection diagram via cloud data center system.
Haiwell Cloud Data Center is a centralized and wireless multi-point data exchange and management service. As long as you use the end device as Haiwell IoT, you can exchange this data from the center through Haiwell Cloud Data Center. Thus, you can connect and collect any HaiwellHMI data to the central HMI. The collected data will be sent via the Internet to which the HMI is connected. For example, we have a device as Center Device, HaiwellHMI(A), HaiwellHMI(B), and HaiwellHMI(C). If we want to send data from HMI B and C to display on device A, we can do it through "Haiwell cloud Data Center".