How does a conductivity probe work ?
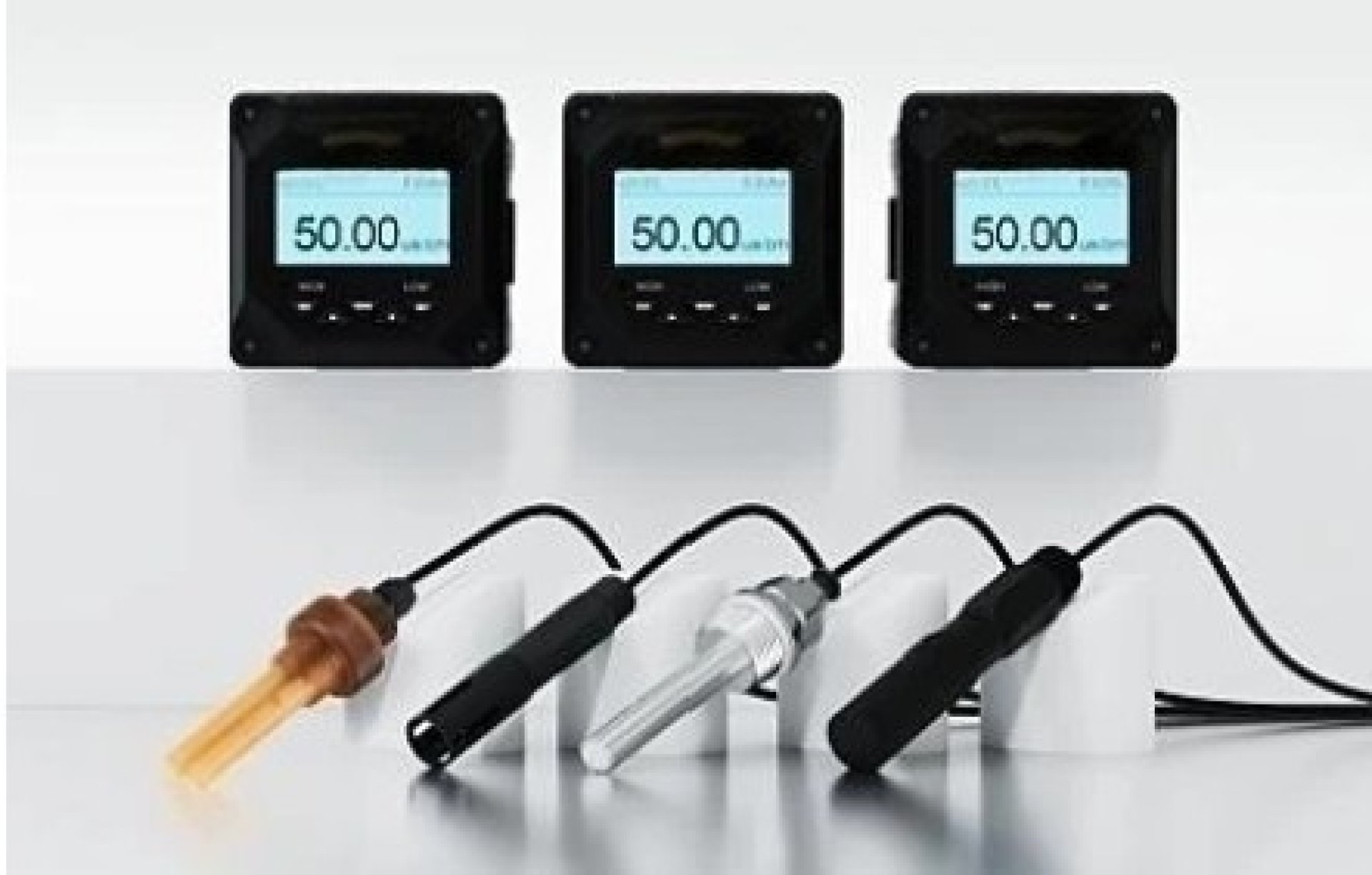

Meaning of "Conductivity"
Conductivity, which refers to the ability of a material to conduct electricity, is a fundamental property in physics, chemistry, and engineering, which plays an important role in many industries.
Conductivity is measured in Siemens units per meter (S/m) and the return value is measured in ohm-meters (Ω·m). Materials with high electrical conductivity conduct electricity well. While materials with low conductivity will be insulating.
- Metals are excellent conductors of electricity, as their atomic structure contains electrons that move freely. This makes it easy for electricity to pass through.
- Insulators such as rubber, plastic, and glass have electrons that hold tightly together. This makes it difficult for the current to pass through.
- Semiconductors have medium conductivity and are sensitive to temperature or additives. It is used in electronic devices such as transistors, diodes,
What is a conductivity probe?
Conductivity probes or EC probes are devices used to measure the conductivity of solutions and play an important role in chemistry, environment, water engineering, agriculture, and water quality measurement.
It consists of electrodes made of conductive materials. When immersed in liquid, there is a flow of current between the electrodes. The conductivity value depends on the amount of ions in the solution. The more ions there are, the higher the value.
Type of probe :
- Two-electrode type is suitable for general measurements in liquids with medium conductivity.
- Four-electrode type is more accurate Reduce Polarization Problems
- Inductive/Contactless: Alternating current, suitable for continuous measurement.
The main elements of the probe
- Electrodes: Parts in contact with liquids. Made of metal or graphite.
- Sensor Body: Prevents damage, usually made of stainless steel or plastic.
- Cell Constant Value: The constant value used to calculate the conductivity value.
- Temperature Sensor: Some models have it to compensate for the effects of temperature.
- Connector: Connected to the display device.
- Calibration Solutions: Used to calibrate to the correct value.
- Conductivity Meter: Displays the measurement value from the probe.
Principle of operation
- Discharge current through electrodes immersed in solution.
- The ions in the solution move along the electrodes.
- The current flowing is caused by the movement of ions.
- Voltage and current measurement system and then calculate conductivity
- Temperature affects the measurement value, so there is a compensation system.
- Results are displayed in S/m or μS/cm.
Types of probes
- 2-pole / 4-pole
- Induction (non-contact)
- Submersible
- Flow-through for high temperatures
- Multiparameter
Calibration
- 1-Point: Uses only one standard, suitable for general applications.
- 2-Point: Uses low and high values for greater accuracy.